Setting up OpenShift Environment
On this Page
Setting up OpenShift Environment¶
The below lists the dependencies required to install HabanaAI Operator on OpenShift:
Note
Before installing the dependencies, make sure to review the supported OpenShift version listed in the Support Matrix.
Installing Kernel Module Management (KMM) Operator¶
The KKM Operator is paired with the HabanaAI Operator to automate the management of all Intel Gaudi software components required for provisioning Gaudi accelerators within the OpenShift cluster, including drivers and monitoring metrics.
You can install the KMM Operator using the RedHat OpenShift console or CLI as described below.
Using RedHat OpenShift Console¶
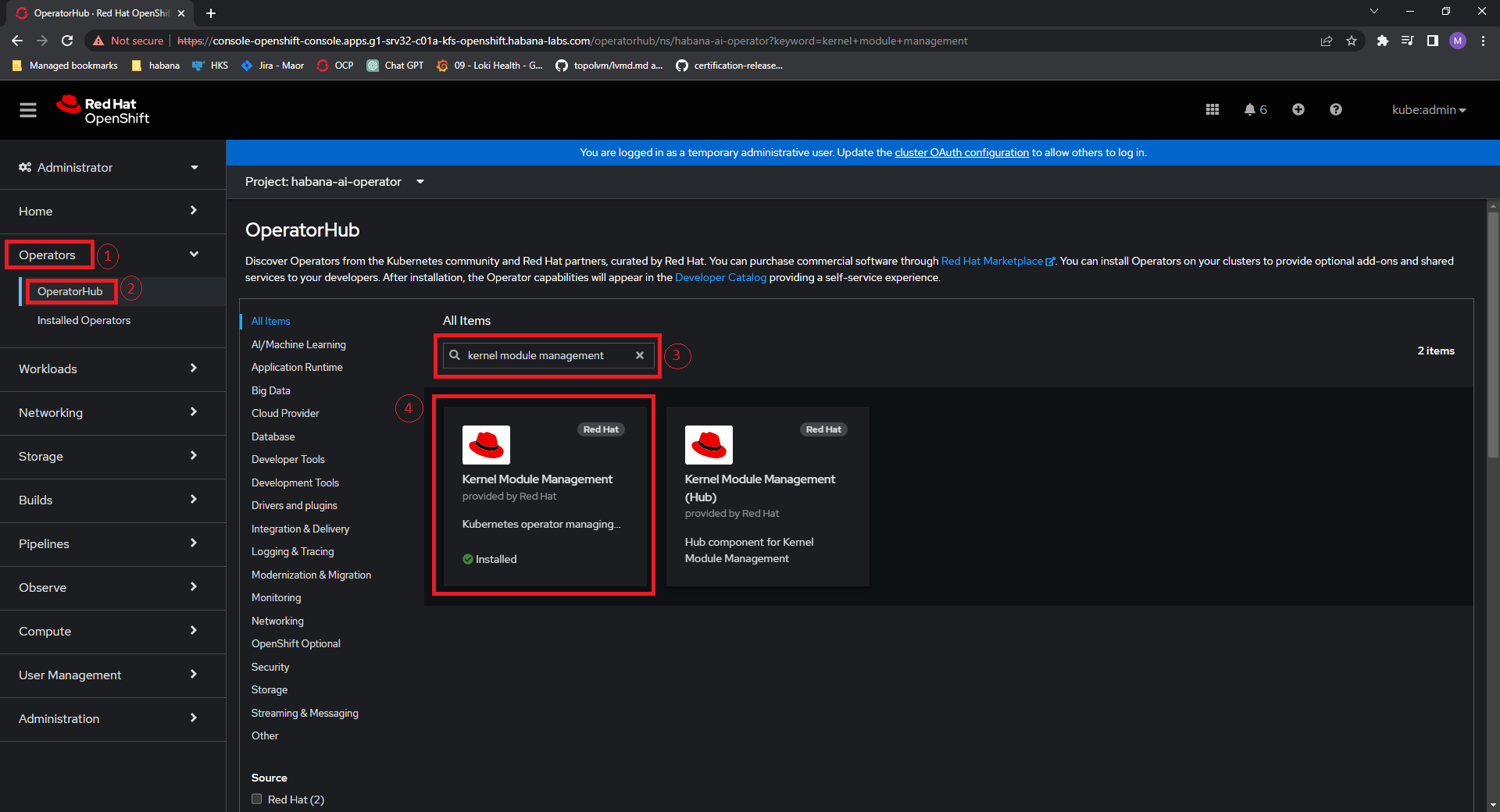
Go to Operators.
Click “OperatorHub”.
In All Items field, search for Kernel Module Management.
Click “Install”.
Using CLI¶
Create
kmm-install.yamlfile containing the following:apiVersion: v1 kind: Namespace metadata: name: openshift-kmm --- apiVersion: operators.coreos.com/v1 kind: OperatorGroup metadata: generateName: openshift-kmm- name: kernel-module-management namespace: openshift-kmm spec: targetNamespaces: - openshift-kmm --- apiVersion: operators.coreos.com/v1alpha1 kind: Subscription metadata: name: kernel-module-management namespace: openshift-kmm spec: channel: "stable" installPlanApproval: Automatic name: kernel-module-management source: redhat-operators sourceNamespace: openshift-marketplace
Apply the yaml file:
oc apply -f kmm-install.yaml
Installing Intel Gaudi Firmware¶
To install Intel Gaudi firmware using the KMM Operator, add /var/lib/firmware
in the firmware search path and run firmware-path.yaml in the CLI as shown below.
For further details, refer to the KMM GitHub Documentation.
Note
The name of the yaml file provided in this section, firmware-path.yaml, is given as an example only.
Create the yaml file with the following content:
apiVersion: machineconfiguration.openshift.io/v1 kind: MachineConfig metadata: labels: machineconfiguration.openshift.io/role: worker name: firmware-path spec: config: ignition: version: 3.2.0 kernelArguments: - 'firmware_class.path=/var/lib/firmware'
Apply the yaml file:
oc apply -f firmware-path.yaml
Installing Node Feature Discovery (NFD) Operator¶
The Node Feature Discovery (NFD) Operator scans the hardware of OpenShift nodes and assigns them with the appropriate labels, ensuring that drivers are exclusively installed on servers that need to use them.
You can install the NFD Operator using the RedHat OpenShift console or by CLI as described below.
Note
While installing the NFD Operator is not mandatory, it is still recommended to have it before installing HabanaAI Operator on OpenShift.
Using RedHat OpenShift Console¶
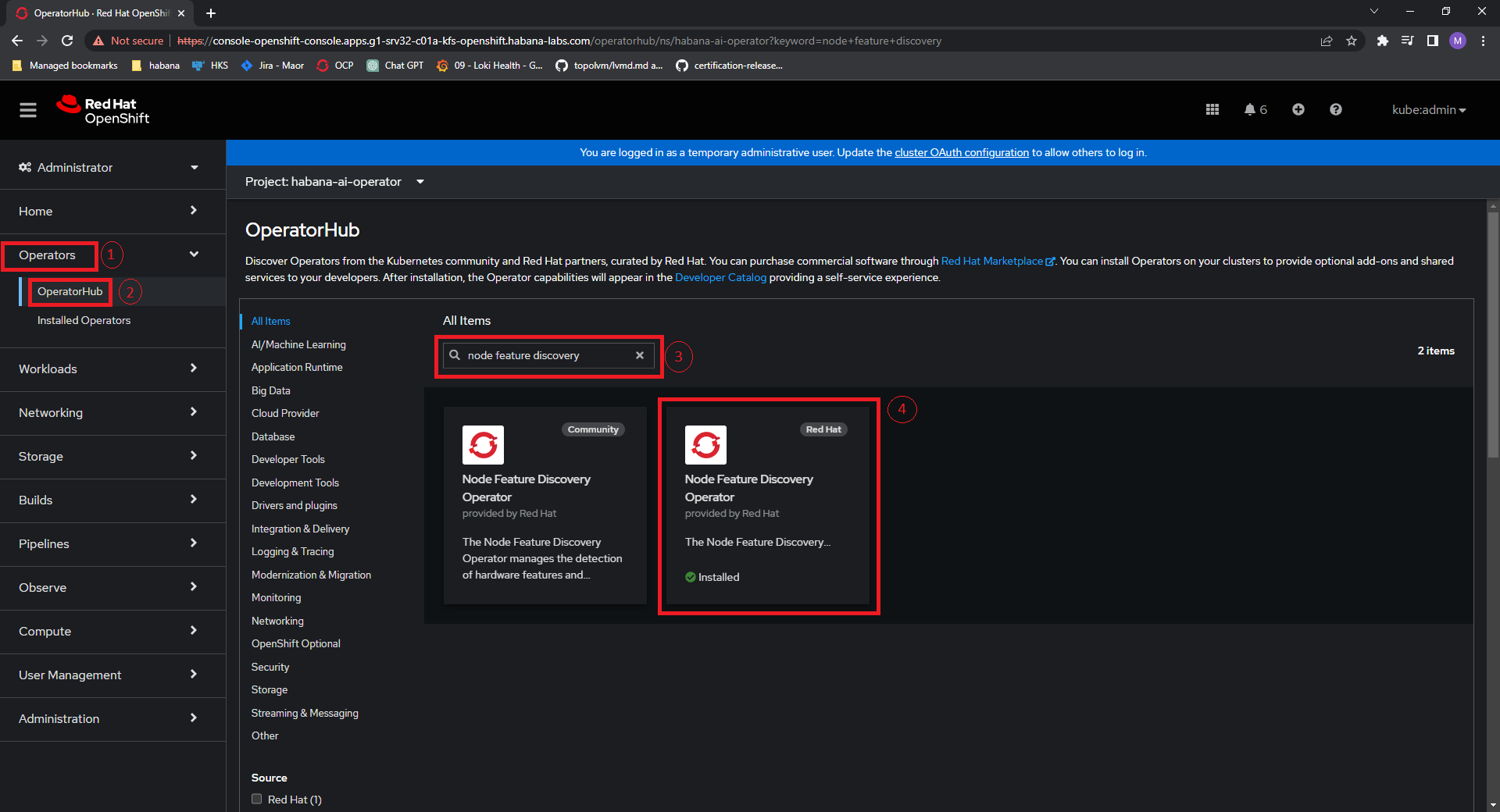
Go to Operators.
Click “OperatorHub”.
In All Items field, search for Node Feature Discovery.
Click “Install”.
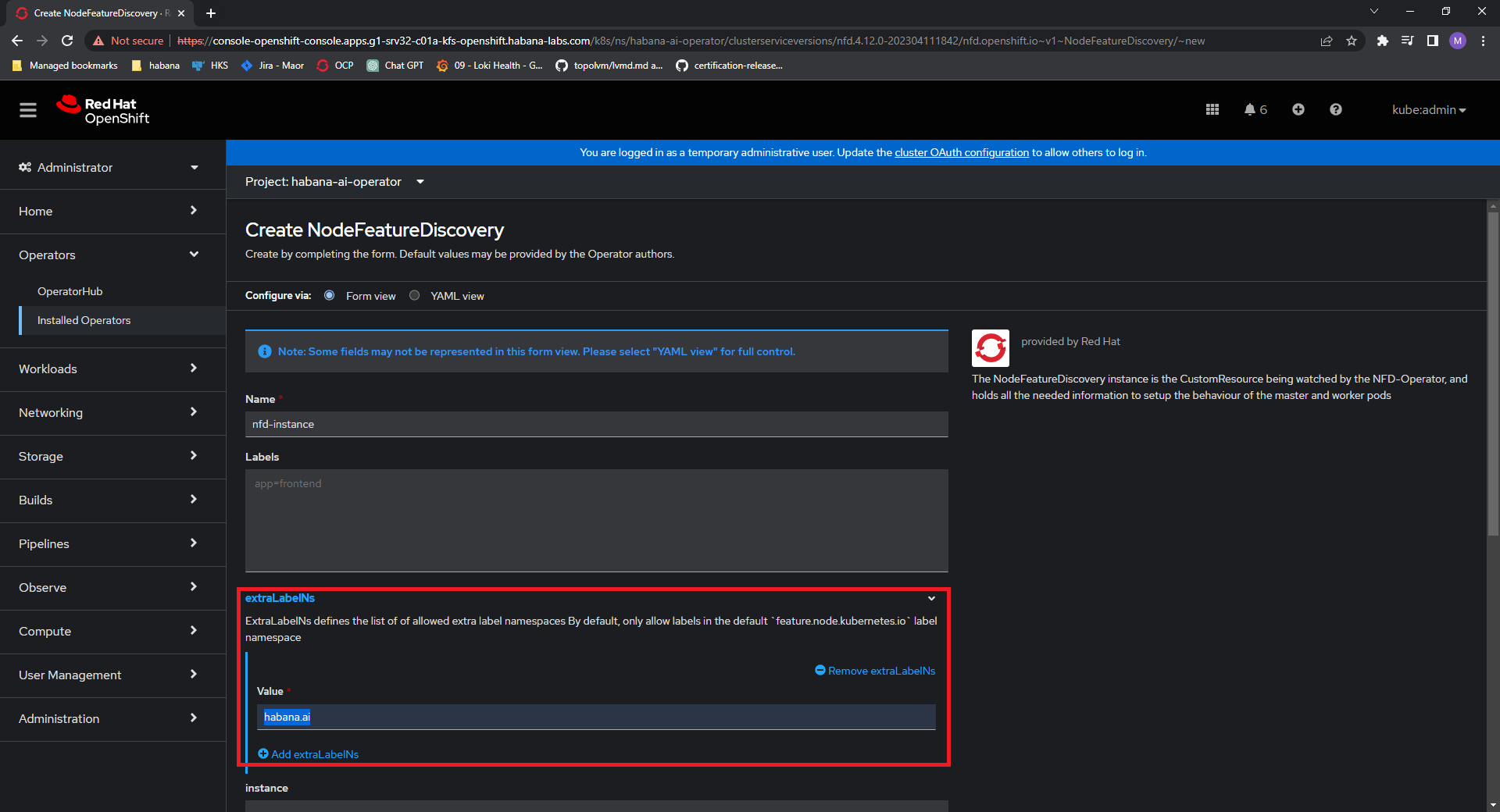
Create an NFD instance and include “habana.ai” in the extraLabelNs list. This facilitates creating HabanaAI-specific labels, which consist of information about the card types inside each Gaudi node.
Using CLI¶
Create
nfd-install.yamlfile containing the following:apiVersion: v1 kind: Namespace metadata: name: openshift-nfd --- apiVersion: operators.coreos.com/v1 kind: OperatorGroup metadata: generateName: openshift-nfd- name: openshift-nfd namespace: openshift-nfd spec: targetNamespaces: - openshift-nfd --- apiVersion: operators.coreos.com/v1alpha1 kind: Subscription metadata: name: nfd namespace: openshift-nfd spec: channel: "stable" installPlanApproval: Automatic name: nfd source: redhat-operators sourceNamespace: openshift-marketplace
Apply the yaml file:
oc apply -f nfd-instance.yaml
Create an NFD instance:
Create
nfd-instance.yamlfile containing the following:apiVersion: nfd.openshift.io/v1 kind: NodeFeatureDiscovery metadata: name: nfd-instance namespace: openshift-nfd spec: customConfig: configData: | # - name: "more.kernel.features" # matchOn: # - loadedKMod: ["example_kmod3"] # - name: "more.features.by.nodename" # value: customValue # matchOn: # - nodename: ["special-.*-node-.*"] extraLabelNs: - habana.ai instance: '' operand: image: >- registry.redhat.io/openshift4/ose-node-feature-discovery@sha256:edd2adfdf423d6a1eb7e8c1e388d9cf5fbc829e7e66c7bc955e9b2a6f50d1a47 servicePort: 12000 topologyupdater: false workerConfig: configData: | core: sleepInterval: 60s sources: pci: deviceClassWhitelist: - "0200" - "03" - "12" deviceLabelFields: - "vendor"
Apply the yaml file:
oc apply -f nfd-instance.yaml
If you would rather not install the NDF operator or add “habana.ai” to the extraLabelNs list,
you can label the HabanaAI nodes as habana.ai/hpu.gaudi.present=true by executing the
following command for each Gaudi node:
oc label node/<NODE> habana.ai/hpu.gaudi.present=true