Memory Scrub Verification Tool
On this Page
Memory Scrub Verification Tool¶
The Memory Scrub Verification (MSV) is a tool designed to ensure that the HBM on the Gaudi device is properly scrubbed during the boot process. Memory scrubbing is crucial in a Hypervisor environment to guarantee that the device is clean of any residual data left by previous usage. This ensures that your workloads are secure and isolated from others, preventing exposure to potentially sensitive information.
The MSV should be executed by the Hypervisor after the previous machine has been destroyed and all Gaudi 3 devices have completed their boot process. This should occur before the kernel-mode driver is loaded.
This section explains how to integrate MSV into your system, covering the process of installing the tool, building the source code and incorporating the executable into the Hypervisor workflow.
Options and Usage¶
The following table lists the available MSV options and their usage to help you effectively configure the tool for your specific needs.
Note
Make sure to unload the driver before using MSV.
Example:
$ sudo hbm_scrubbing_validator -busId 0000:09:00.0 -num_of_samples 1000 -sample_size 2 -o /home/user/failed_addresses.txt
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Specifies number of logical blocks to validate. The number of blocks corresponds to the number of samples, with each sample representing a continuous memory patch used to verify that memory scrubbing was performed. The size of each block is calculated as 128GB/num_of_samples (where 128GB is the total HBM size). Must be greater than 0. Default is 1. |
|
Specifies sample size. The size represents the number of consecutive addresses validated in each block. For example, setting 4 will check 4X128b patches within each sample. Must be greater than 0. Default is 1. |
|
Specifies number of retries until boot is complete. The HBM scrubbing tool is operated by the Hypervisor system which needs to know that the tested devices already finished the boot stage. This parameter defines how many retries to perform to validate the boot process. Default is 12 (each retry takes 5 seconds). |
|
Path to the output file that will contain the addresses which failed validation. This parameter defines the path to the file which will contain offending addresses met during testing of the device. |
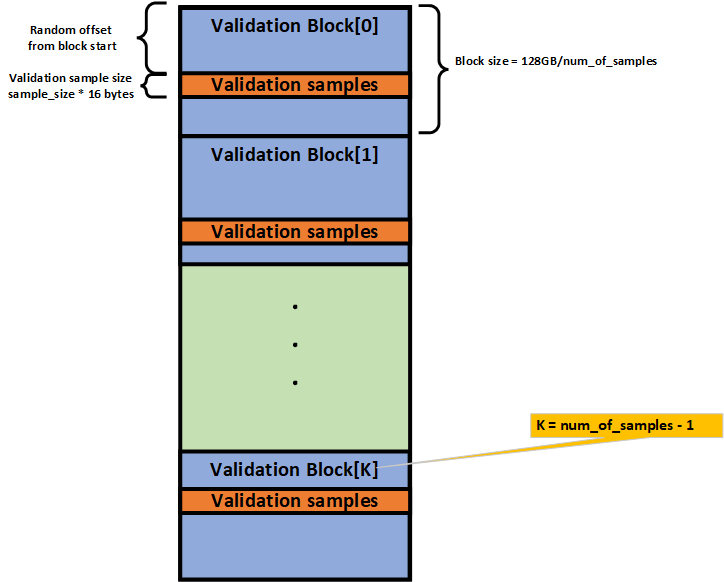
Figure 22 Validation Samples and Blocks in MSV¶
Output examples:
Success output example:
$ sudo hbm_scrubbing_validator -busId 0000:09:00.0 -num_of_samples 10000 -sample_size 4 The boot process is complete, going to validate hbm scrubbing. Number of failed reads: 0
Failure output example:
$ sudo hbm_scrubbing_validator -busId 0000:21:00.0 -num_of_samples 100000 -sample_size 8 -o /root/logs/failed_addresses.txt The boot process is complete, going to validate hbm scrubbing. Number of failed reads: 32
The MSV writes the failed validation addresses to ‘/root/logs/failed_addresses.txt’ as follows:
$ cat /root/logs/failed_addresses.txt 2010000000184f0 2010000000184f4 2010000000184f8 2010000000184fc 201000000018500 201000000018504 .....
Error Codes¶
The following lists the MSV return codes.
Code |
Status |
Description |
|---|---|---|
0 |
SUCCESS |
All addresses validated successfully. |
1 |
PERMISSION_DENIED |
Failed - program was executed without root privileges. |
2 |
WRONG_ARGS |
Failed - incorrect arguments provided. |
3 |
SETUP_FAILED |
Failed - could not initialize the device. |
4 |
BOOT_NOT_READY |
Failed - exceeded maximum retries while waiting for the device to be ready (boot). |
5 |
VALIDATION_FAILED |
Validation failed - at least one address does not match the scrubbing pattern. |
